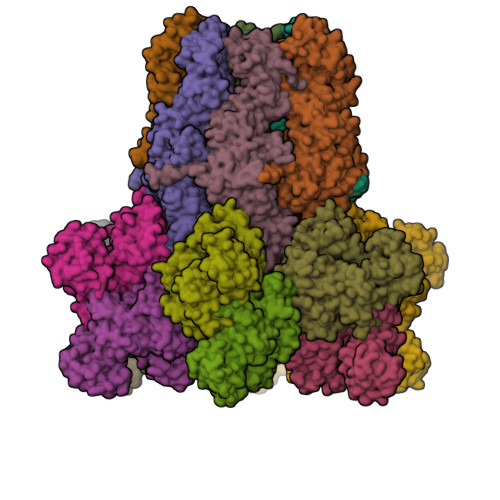
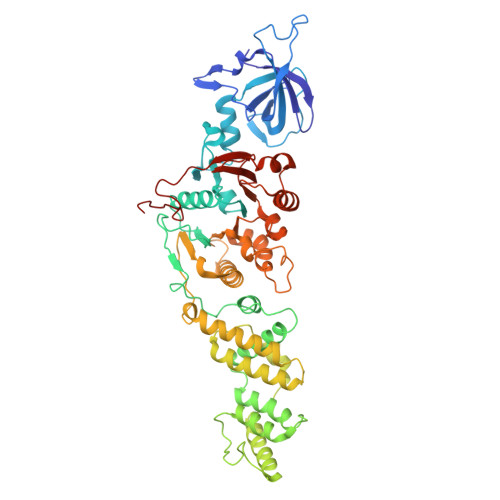
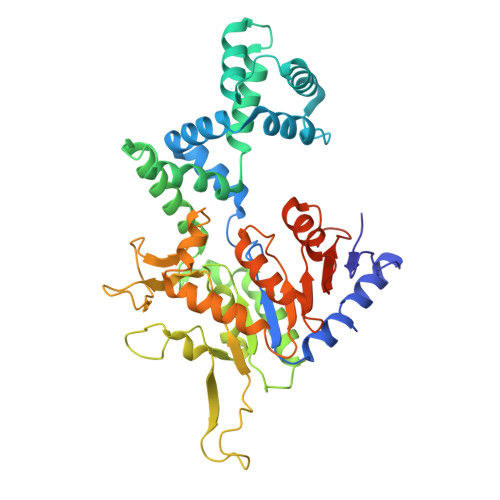
Mechanistic basis for the allosteric activation of NADase activity in the Sir2-HerA antiphage defense system.
Zhen, X., Zhou, B., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Zhao, H., Wu, S., Li, Z., Liang, J., Zhang, W., Zhu, Q., He, J., Xiong, X., Ouyang, S.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 9269-9269
- PubMed: 39465277
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53614-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YHO, 8YHX - PubMed Abstract:
Sir2-HerA is a widely distributed antiphage system composed of a RecA-like ATPase (HerA) and an effector with potential NADase activity (Sir2). Sir2-HerA is believed to provide defense against phage infection in Sir2-dependent NAD + depletion to arrest the growth of infected cells. However, the detailed mechanism underlying its antiphage activity remains largely unknown. Here, we report functional investigations of Sir2-HerA from Staphylococcus aureus (SaSir2-HerA), unveiling that the NADase function of SaSir2 can be allosterically activated by the binding of SaHerA, which then assembles into a supramolecular complex with NADase activity. By combining the cryo-EM structure of SaSir2-HerA in complex with the NAD + cleavage product, it is surprisingly observed that Sir2 protomers that interact with HerA are in the activated state, which is due to the opening of the α15-helix covering the active site, allowing NAD + to access the catalytic pocket for hydrolysis. In brief, our study provides a comprehensive view of an allosteric activation mechanism for Sir2 NADase activity in the Sir2-HerA immune system.
Organizational Affiliation:
Kev Laboratory of Microbial Pathogenesis and Interventions of Fuian Province University, the Key Laboratory of inmate lmmune Biology of Fuijian Province, Biomedical Research Center of South China, Key Laboratory of Opto Electronic Science and Technology for Medicine of the Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, 350117, China.