Identification and characterisation of new inhibitors for the human hematopoietic prostaglandin D(2) synthase
Weber, J.E., Oakley, A.J., Christ, A.N., Clark, A.G., Hayes, J.D., Hall, R., Hume, D.A., Board, P.G., Smythe, M.L., Flanagan, J.U.(2010) Eur J Med Chem 45: 447-454
- PubMed: 19939518
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.10.025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EE2 - PubMed Abstract:
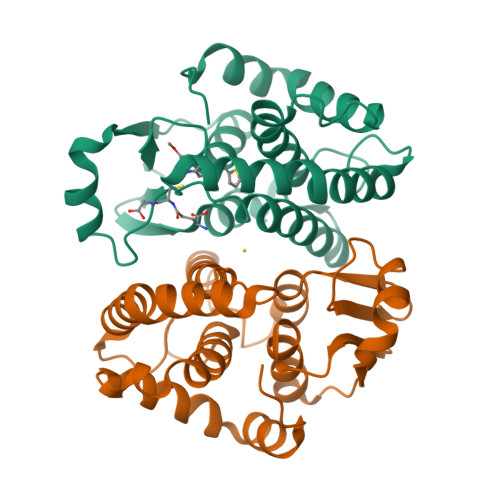
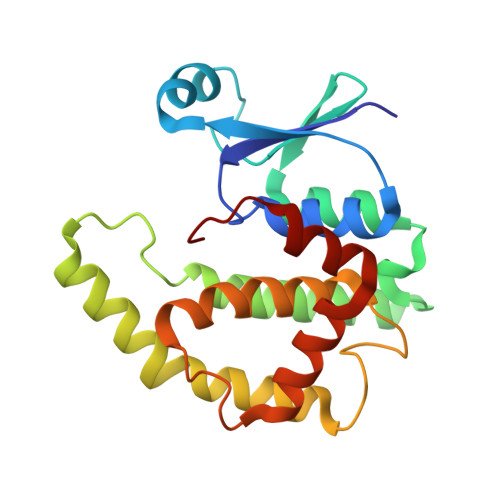
Prostaglandin D(2) synthesised by the hematopoietic prostaglandin D(2) synthase has a pro-inflammatory effect in allergic asthma, regulating many hallmark characteristics of the disease. Here we describe identification of hematopoietic prostaglandin D(2) synthase inhibitors including cibacron blue, bromosulfophthalein and ethacrynic acid. Expansion around the drug-like ethacrynic acid identified a novel inhibitor, nocodazole, and a fragment representing its aromatic core. Nocodazole binding was further characterised by docking calculations in combination with conformational strain analysis. The benzyl thiophene core was predicted to be buried in the active site, binding in the putative prostaglandin binding site, and a likely hydrogen bond donor site identified. X-ray crystallographic studies supported the predicted binding mode.
Organizational Affiliation:
The University of Queensland, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, Building 80, St Lucia, Queensland 4072, Australia.