Biophysical Characterization of a Novel Phosphopentomutase from the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis .
Naz, Z., Lubkowski, J., Saleem, M., Aslam, M., Rahman, M., Wlodawer, A., Rashid, N.(2024) Int J Mol Sci 25
- PubMed: 39684607
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312893
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9IX8 - PubMed Abstract:
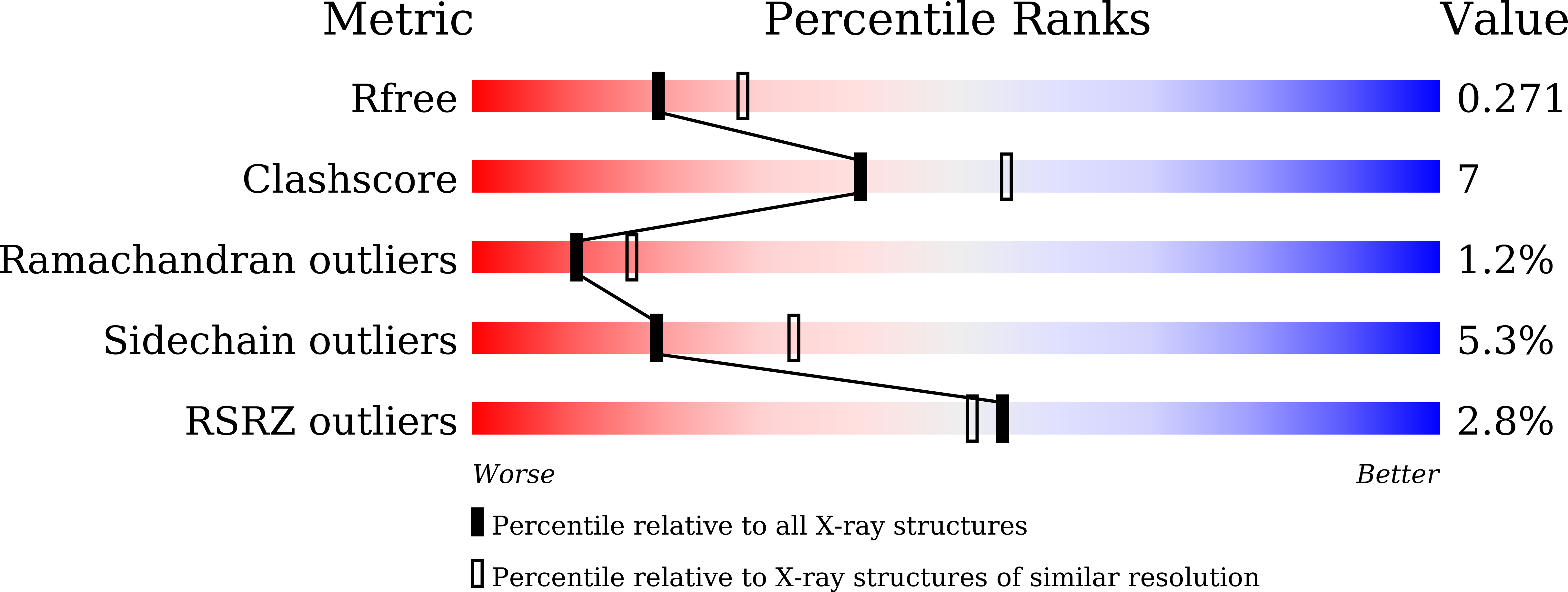
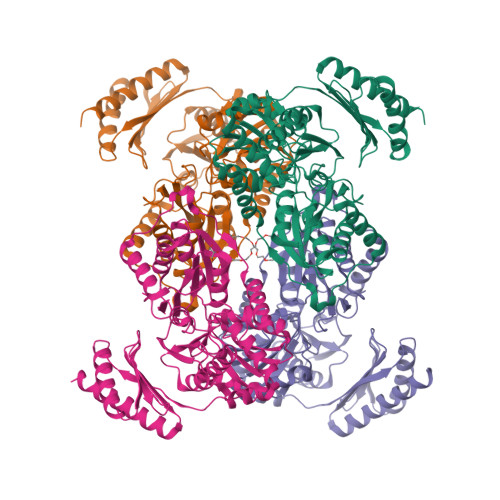
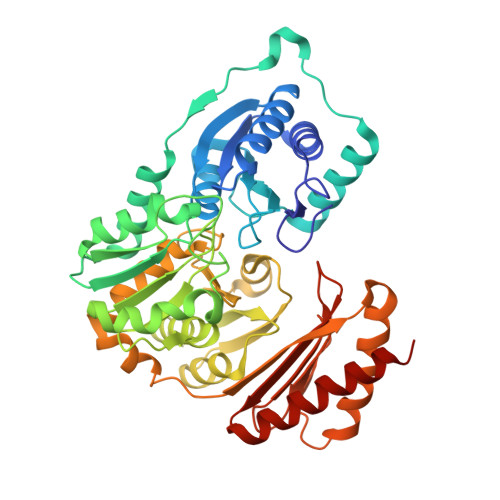
Phosphopentomutases catalyze the isomerization of ribose 1-phosphate and ribose 5-phosphate. Thermococcus kodakarensis , a hyperthermophilic archaeon, harbors a novel enzyme (PPM Tk ) that exhibits high homology with phosphohexomutases but has no significant phosphohexomutase activity. Instead, PPM Tk catalyzes the interconversion of ribose 1-phosphate and ribose 5-phosphate. Here, we report biophysical analysis, crystallization, and three-dimensional structure determination of PPM Tk by X-ray diffraction at 2.39 Å resolution. The solved structure revealed a novel catalytic motif, unique to PPM Tk , which makes this enzyme distinct from the homologous counterparts. We postulate that this novel catalytic motif may enable PPM Tk to isomerize phosphopentose instead of phosphohexose. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first biophysical and structural analysis of a phosphopentomutase from hyperthermophilic archaea.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, University of the Punjab, Lahore 54590, Pakistan.