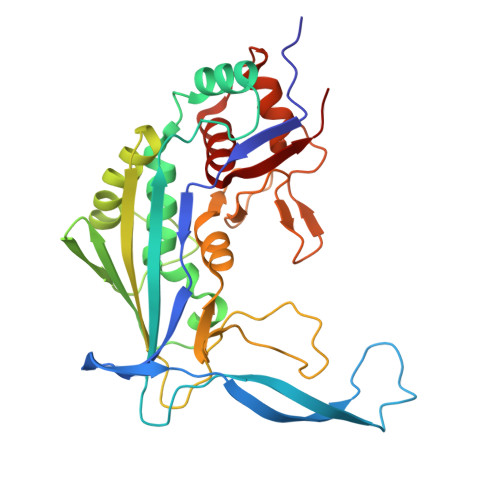
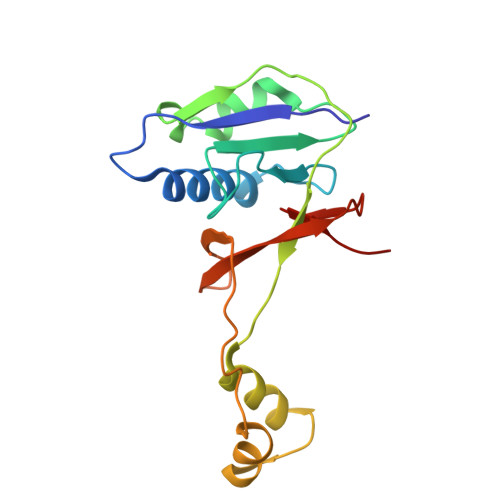
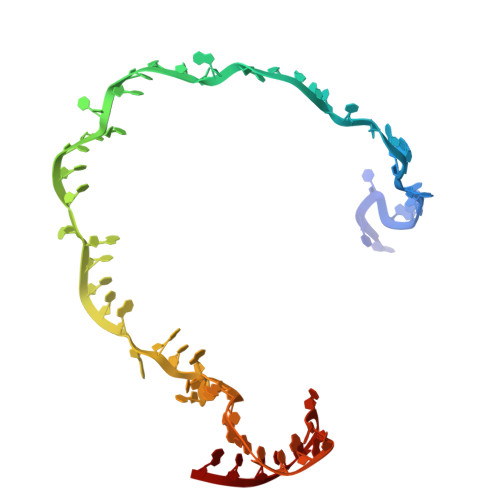
Cas1 mediates the interference stage in a phage-encoded CRISPR-Cas system.
Zhang, L., Wang, H., Zeng, J., Cao, X., Gao, Z., Liu, Z., Li, F., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., Feng, Y.(2024) Nat Chem Biol 20: 1471-1481
- PubMed: 38977786
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-024-01659-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8K0H, 8K0J, 8K0K - PubMed Abstract:
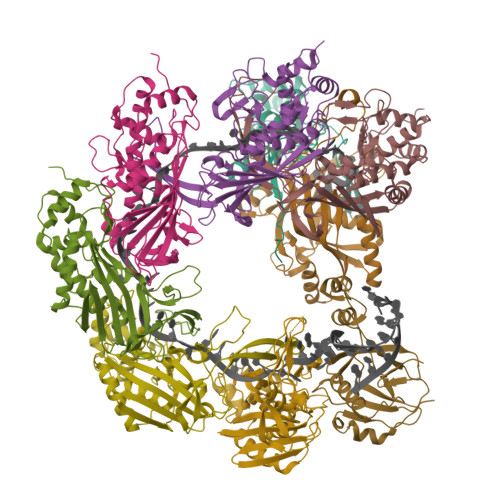
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Cas systems are prokaryotic adaptive immune systems against invading phages and other mobile genetic elements. Notably, some phages, including the Vibrio cholerae-infecting ICP1 (International Center for Diarrheal Disease Research, Bangladesh cholera phage 1), harbor CRISPR-Cas systems to counteract host defenses. Nevertheless, ICP1 Cas8f lacks the helical bundle domain essential for recruitment of helicase-nuclease Cas2/3 during target DNA cleavage and how this system accomplishes the interference stage remains unknown. Here, we found that Cas1, a highly conserved component known to exclusively work in the adaptation stage, also mediates the interference stage through connecting Cas2/3 to the DNA-bound CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (Cascade; CRISPR system yersinia, Csy) of the ICP1 CRISPR-Cas system. A series of structures of Csy, Csy-dsDNA (double-stranded DNA), Cas1-Cas2/3 and Csy-dsDNA-Cas1-Cas2/3 complexes reveal the whole process of Cas1-mediated target DNA cleavage by the ICP1 CRISPR-Cas system. Together, these data support an unprecedented model in which Cas1 mediates the interference stage in a phage-encoded CRISPR-Cas system and the study also sheds light on a unique model of primed adaptation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Protein Science, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure, Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.