Discovery of EEDi-5273 as an Exceptionally Potent and Orally Efficacious EED Inhibitor Capable of Achieving Complete and Persistent Tumor Regression.
Rej, R.K., Wang, C., Lu, J., Wang, M., Petrunak, E., Zawacki, K.P., McEachern, D., Yang, C.Y., Wang, L., Li, R., Chinnaswamy, K., Wen, B., Sun, D., Stuckey, J.A., Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Tang, G., Wang, S.(2021) J Med Chem 64: 14540-14556
- PubMed: 34613724
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01059
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
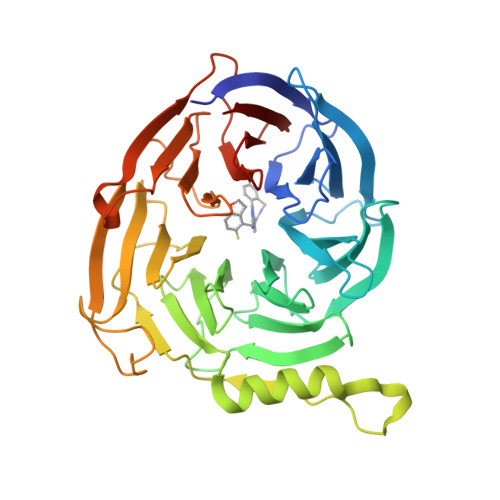
7MSB, 7MSD - PubMed Abstract:
Embryonic ectoderm development (EED) is a promising therapeutic target for human cancers and other diseases. We report herein the discovery of exceptionally potent and efficacious EED inhibitors. By conformational restriction of a previously reported EED inhibitor, we obtained a potent lead compound. Further optimization of the lead yielded exceptionally potent EED inhibitors. The best compound EEDi-5273 binds to EED with an IC 50 value of 0.2 nM and inhibits the KARPAS422 cell growth with an IC 50 value of 1.2 nM. It demonstrates an excellent PK and ADME profile, and its oral administration leads to complete and persistent tumor regression in the KARPAS422 xenograft model with no signs of toxicity. Co-crystal structures of two potent EED inhibitors with EED provide a solid structural basis for their high-affinity binding. EEDi-5273 is a promising EED inhibitor for further advanced preclinical development for the treatment of human cancer and other human diseases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee 38163, United States.