Structural basis of the activation of type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor.
Li, J., Choi, E., Yu, H., Bai, X.C.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 4567-4567
- PubMed: 31594955
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12564-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PYH - PubMed Abstract:
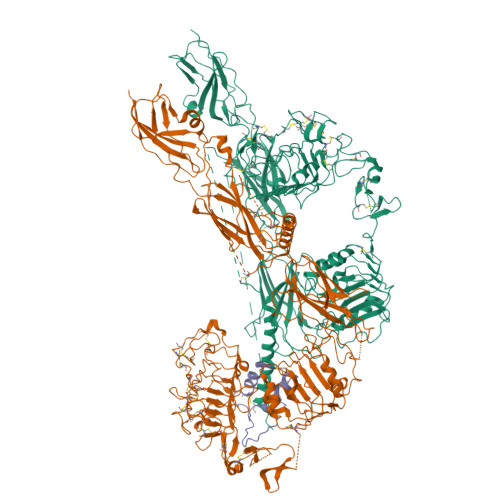
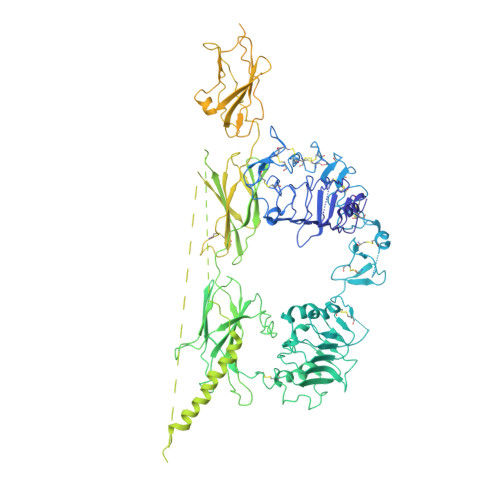
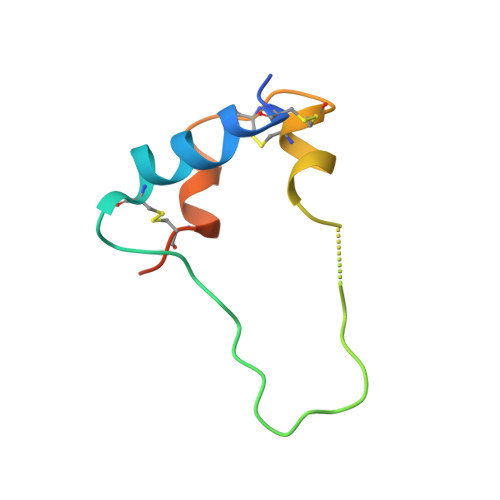
Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth and proliferation, and can be activated by IGF1, IGF2, and insulin. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of full-length IGF1R-IGF1 complex in the active state. This structure reveals that only one IGF1 molecule binds the Γ-shaped asymmetric IGF1R dimer. The IGF1-binding site is formed by the L1 and CR domains of one IGF1R protomer and the α-CT and FnIII-1 domains of the other. The liganded α-CT forms a rigid beam-like structure with the unliganded α-CT, which hinders the conformational change of the unliganded α-CT required for binding of a second IGF1 molecule. We further identify an L1-FnIII-2 interaction that mediates the dimerization of membrane-proximal domains of IGF1R. This interaction is required for optimal receptor activation. Our study identifies a source of the negative cooperativity in IGF1 binding to IGF1R and reveals the structural basis of IGF1R activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.