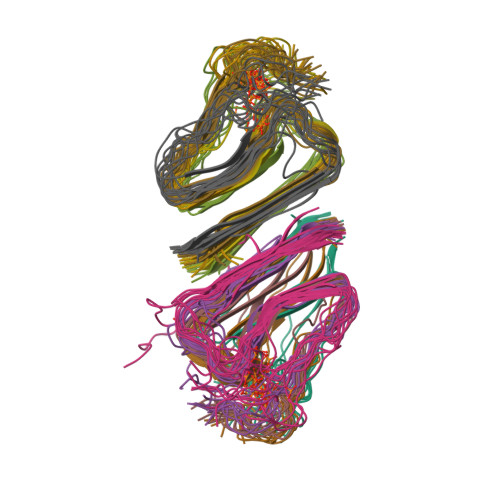
Molecular structure of an N-terminal phosphorylated beta-amyloid fibril.
Hu, Z.W., Vugmeyster, L., Au, D.F., Ostrovsky, D., Sun, Y., Qiang, W.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 11253-11258
- PubMed: 31097588
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818530116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OC9 - PubMed Abstract:
The structural polymorphism in β-amyloid (Aβ) plaques from Alzheimer disease (AD) has been recognized as an important pathological factor. Plaques from sporadic AD patients contain fibrillar deposits of various amyloid proteins/peptides, including posttranslational modified Aβ (PTM-Aβ) subtypes. Although many PTM-Aβs were shown to accelerate the fibrillation process, increase neuronal cytotoxicity of aggregates, or enhance the stability of fibrils, the contribution of PTM-Aβs to structural polymorphisms and their pathological roles remains unclear. We report here the NMR-based structure for the Ser-8-phosphorylated 40-residue Aβ (pS8-Aβ 40 ) fibrils, which shows significant difference to the wild-type fibrils, with higher cross-seeding efficiency and thermodynamic stability. Given these physicochemical properties, the structures originated from pS8-Aβ 40 fibrils may potentially dominate the polymorphisms in the mixture of wild-type and phosphorylated Aβ deposits. Our results imply that Aβ subtypes with "seeding-prone" properties may influence the polymorphisms of amyloid plaques through the cross-seeding process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Binghamton University, Binghamton, NY 13902.