Structure-Based Engineering of an Artificially Generated NADP+-Dependent d-Amino Acid Dehydrogenase
Hayashi, J., Seto, T., Akita, H., Watanabe, M., Hoshino, T., Yoneda, K., Ohshima, T., Sakuraba, H.(2017) Appl Environ Microbiol 83
- PubMed: 28363957
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00491-17
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GZ1, 5GZ3, 5GZ6 - PubMed Abstract:
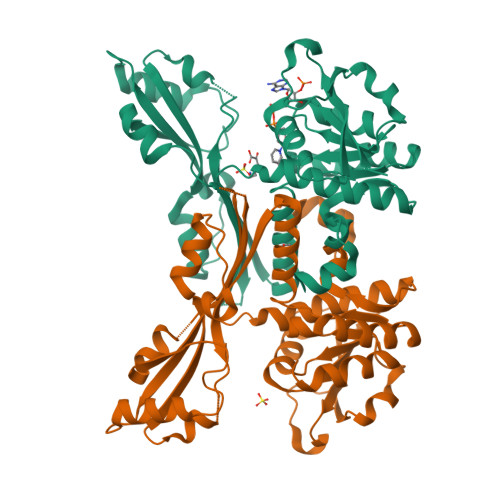
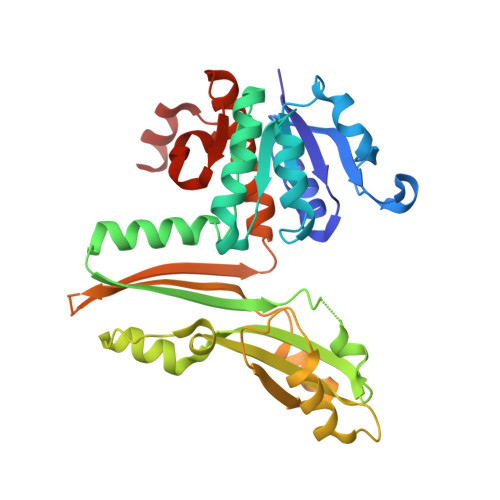
A stable NADP + -dependent d-amino acid dehydrogenase (DAADH) was recently created from Ureibacillus thermosphaericus meso -diaminopimelate dehydrogenase through site-directed mutagenesis. To produce a novel DAADH mutant with different substrate specificity, the crystal structure of apo-DAADH was determined at a resolution of 1.78 Å, and the amino acid residues responsible for the substrate specificity were evaluated using additional site-directed mutagenesis. By introducing a single D94A mutation, the enzyme's substrate specificity was dramatically altered; the mutant utilized d-phenylalanine as the most preferable substrate for oxidative deamination and had a specific activity of 5.33 μmol/min/mg at 50°C, which was 54-fold higher than that of the parent DAADH. In addition, the specific activities of the mutant toward d-leucine, d-norleucine, d-methionine, d-isoleucine, and d-tryptophan were much higher (6 to 25 times) than those of the parent enzyme. For reductive amination, the D94A mutant exhibited extremely high specific activity with phenylpyruvate (16.1 μmol/min/mg at 50°C). The structures of the D94A-Y224F double mutant in complex with NADP + and in complex with both NADPH and 2-keto-6-aminocapronic acid (lysine oxo-analogue) were then determined at resolutions of 1.59 Å and 1.74 Å, respectively. The phenylpyruvate-binding model suggests that the D94A mutation prevents the substrate phenyl group from sterically clashing with the side chain of Asp94. A structural comparison suggests that both the enlarged substrate-binding pocket and enhanced hydrophobicity of the pocket are mainly responsible for the high reactivity of the D94A mutant toward the hydrophobic d-amino acids with bulky side chains. IMPORTANCE In recent years, the potential uses for d-amino acids as source materials for the industrial production of medicines, seasonings, and agrochemicals have been growing. To date, several methods have been used for the production of d-amino acids, but all include tedious steps. The use of NAD(P) + -dependent d-amino acid dehydrogenase (DAADH) makes single-step production of d-amino acids from oxo-acid analogs and ammonia possible. We recently succeeded in creating a stable DAADH and demonstrated that it is applicable for one-step synthesis of d-amino acids, such as d-leucine and d-isoleucine. As the next step, the creation of an enzyme exhibiting different substrate specificity and higher catalytic efficiency is a key to the further development of d-amino acid production. In this study, we succeeded in creating a novel mutant exhibiting extremely high catalytic activity for phenylpyruvate amination. Structural insight into the mutant will be useful for further improvement of DAADHs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied Biological Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Kagawa University, Miki-cho, Kita-gun, Kagawa, Japan.