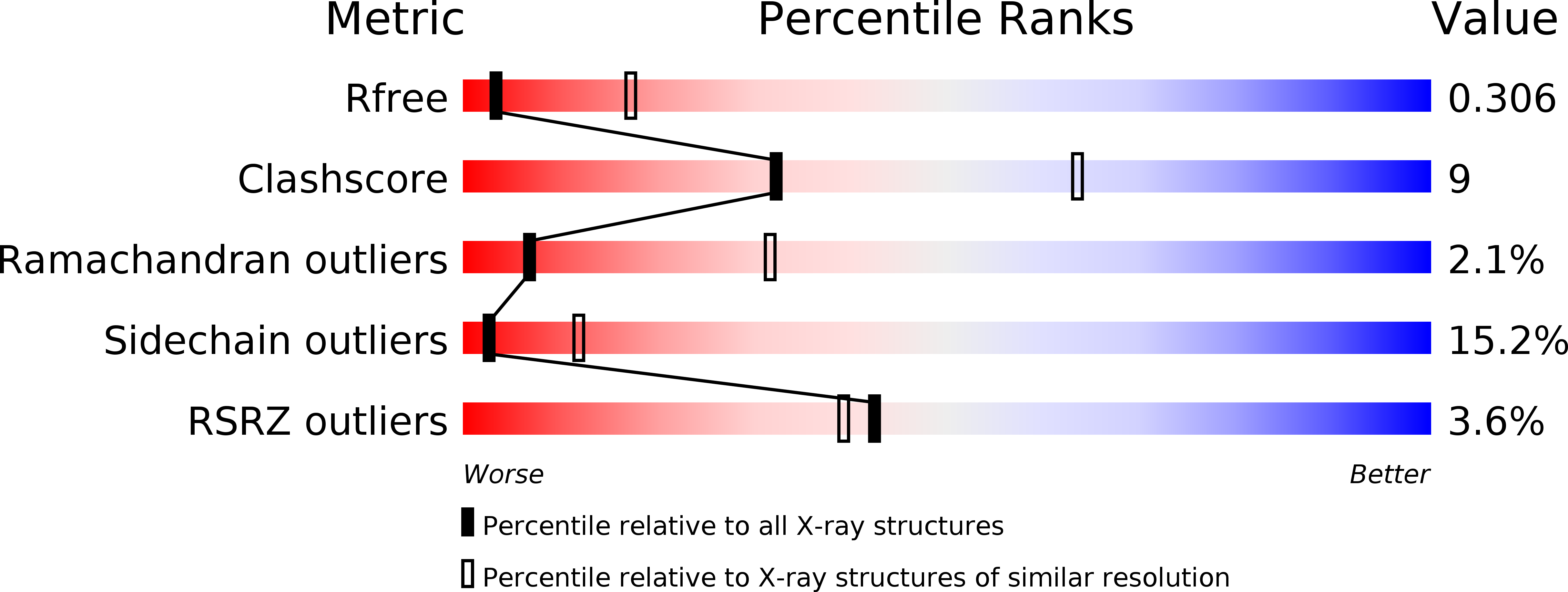
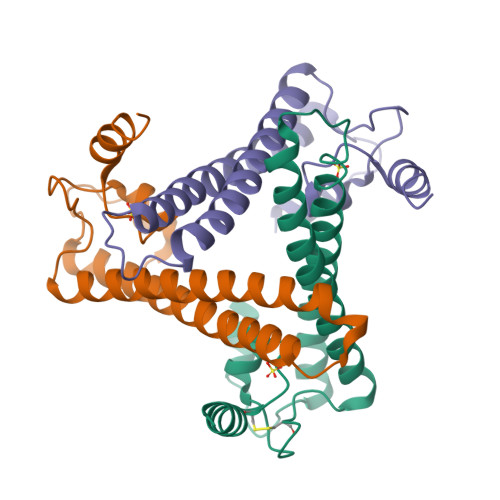
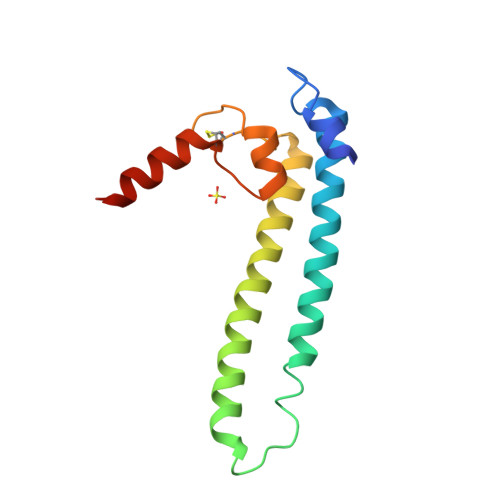
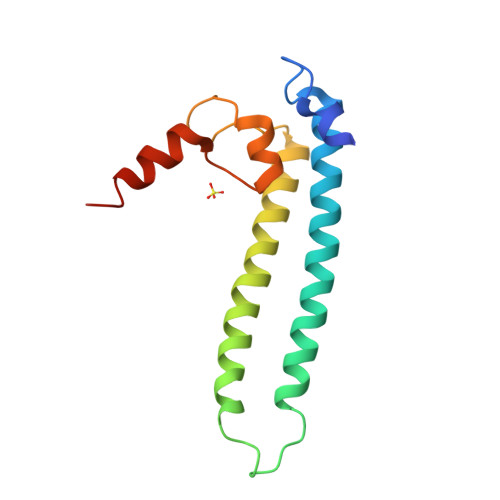
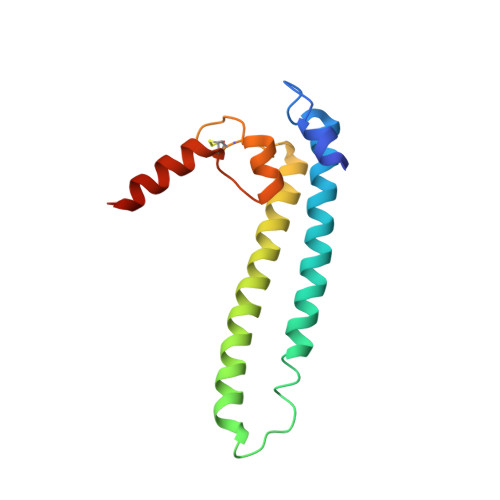
DksA2, a zinc-independent structural analog of the transcription factor DksA.
Furman, R., Biswas, T., Danhart, E.M., Foster, M.P., Tsodikov, O.V., Artsimovitch, I.(2013) FEBS Lett 587: 614-619
- PubMed: 23416301
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.073
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IJJ - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription factor DksA contains a four-Cys Zn(2 +)-finger motif thought to be responsible for structural integrity and the relative disposition of its domains. Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes an additional DksA paralog (DksA2) that is expressed selectively under Zn(2+) limitation. Although DksA2 does not bind Zn(2+), it complements the Escherichia coli dksA deletion and has similar effects on transcription in vitro. In this study, structural and biochemical analyses reveal that DksA2 has a similar fold, domain structure and RNA polymerase binding properties to those of the E. coli DksA despite the lack of the stabilizing metal ion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA.