ACET is a highly potent and specific kainate receptor antagonist: characterisation and effects on hippocampal mossy fibre function.
Dargan, S.L., Clarke, V.R., Alushin, G.M., Sherwood, J.L., Nistico, R., Bortolotto, Z.A., Ogden, A.M., Bleakman, D., Doherty, A.J., Lodge, D., Mayer, M.L., Fitzjohn, S.M., Jane, D.E., Collingridge, G.L.(2009) Neuropharmacology 56: 121-130
- PubMed: 18789344
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
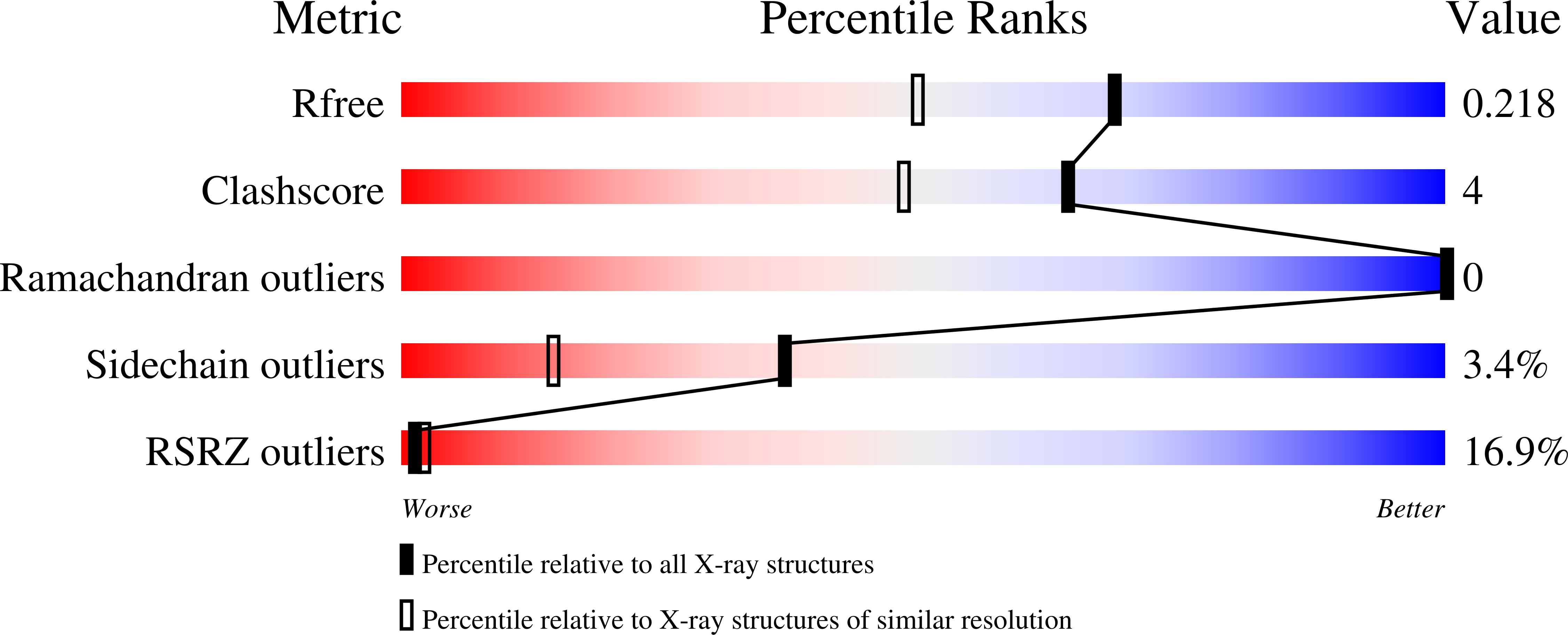
2QS3 - PubMed Abstract:
Kainate receptors (KARs) are involved in both NMDA receptor-independent long-term potentiation (LTP) and synaptic facilitation at mossy fibre synapses in the CA3 region of the hippocampus. However, the identity of the KAR subtypes involved remains controversial. Here we used a highly potent and selective GluK1 (formerly GluR5) antagonist (ACET) to elucidate roles of GluK1-containing KARs in these synaptic processes. We confirmed that ACET is an extremely potent GluK1 antagonist, with a Kb value of 1.4+/-0.2 nM. In contrast, ACET was ineffective at GluK2 (formerly GluR6) receptors at all concentrations tested (up to 100 microM) and had no effect at GluK3 (formerly GluR7) when tested at 1 microM. The X-ray crystal structure of ACET bound to the ligand binding core of GluK1 was similar to the UBP310-GluK1 complex. In the CA1 region of hippocampal slices, ACET was effective at blocking the depression of both fEPSPs and monosynaptically evoked GABAergic transmission induced by ATPA, a GluK1 selective agonist. In the CA3 region of the hippocampus, ACET blocked the induction of NMDA receptor-independent mossy fibre LTP. To directly investigate the role of pre-synaptic GluK1-containing KARs we combined patch-clamp electrophysiology and 2-photon microscopy to image Ca2+ dynamics in individual giant mossy fibre boutons. ACET consistently reduced short-term facilitation of pre-synaptic calcium transients induced by 5 action potentials evoked at 20-25Hz. Taken together our data provide further evidence for a physiological role of GluK1-containing KARs in synaptic facilitation and LTP induction at mossy fibre-CA3 synapses.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Centre for Synaptic Plasticity, University of Bristol, Bristol BS8 1TD, UK. [email protected]