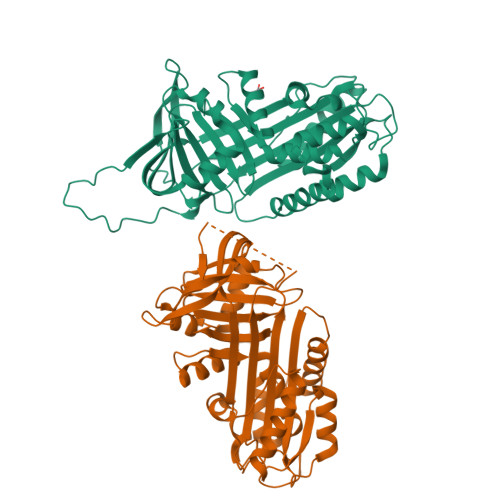
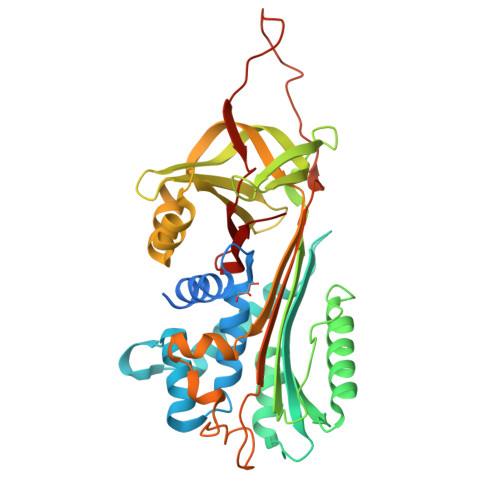
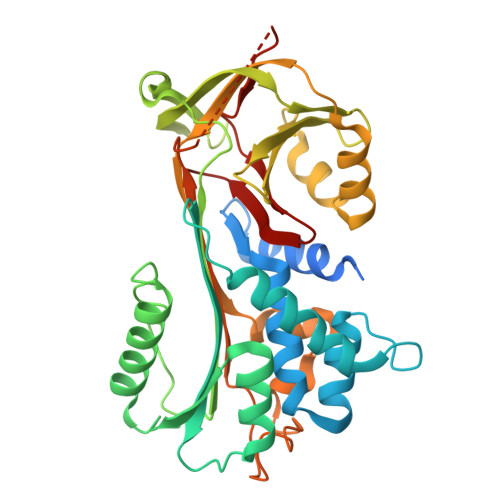
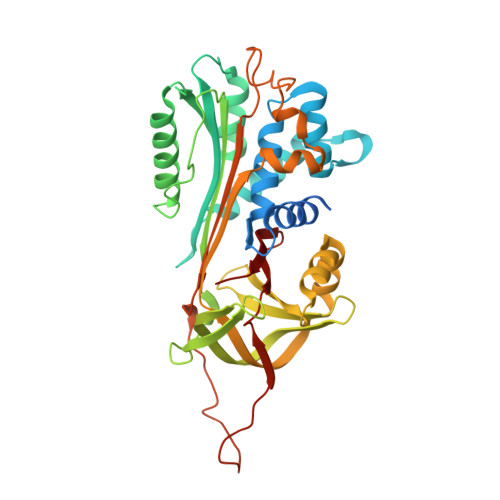
Structure of native protein C inhibitor provides insight into its multiple functions.
Li, W., Adams, T.E., Kjellberg, M., Stenflo, J., Huntington, J.A.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 13759-13768
- PubMed: 17337440
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701074200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HI9, 2OL2 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein C inhibitor (PCI) is a multifunctional serpin with wide ranging protease inhibitory functions, unique cofactor binding activities, and potential non-inhibitory functions akin to the hormone-transporting serpins. To gain insight into the molecular mechanisms utilized by PCI we developed a robust expression system in Escherichia coli and solved the crystal structure of PCI in its native state. The five monomers obtained from our two crystal forms provide an NMR-like ensemble revealing regions of inherent flexibility. The reactive center loop (RCL) of PCI is long and highly flexible with no evidence of hinge region incorporation into beta-sheet A, as seen for other heparin-binding serpins. We adapted an extrinsic fluorescence method for determining dissociation constants for heparin and find that the N-terminal tail of PCI and residues adjacent to helix H are not involved in heparin binding. The minimal heparin length capable of tight binding to PCI was determined to be chains of eight monosaccharide units. A large hydrophobic pocket occupied by hydrophobic crystal contacts was found in an analogous position to the hormone-binding site in thyroxine-binding globulin. In conclusion, the data presented here provide important insights into the mechanisms by which PCI exercises its multiple inhibitory and non-inhibitory functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Haematology, Division of Structural Medicine, Thrombosis Research Unit, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research, University of Cambridge, Wellcome Trust/MRC Building, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2XY, United Kingdom.