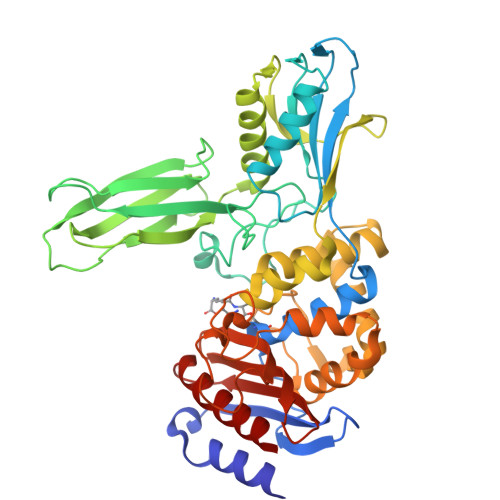
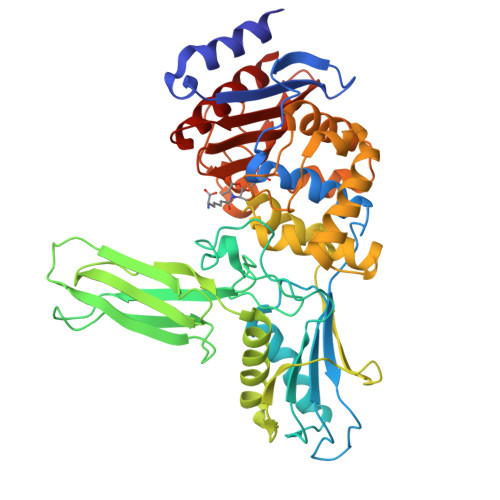
Crystal structure of the Bacillus subtilis penicillin-binding protein 4a, and its complex with a peptidoglycan mimetic peptide.
Sauvage, E., Duez, C., Herman, R., Kerff, F., Petrella, S., Anderson, J.W., Adediran, S.A., Pratt, R.F., Frere, J.M., Charlier, P.(2007) J Mol Biology 371: 528-539
- PubMed: 17582436
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.071
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1W5D, 2J9P - PubMed Abstract:
The genome of Bacillus subtilis encodes 16 penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) involved in the synthesis and/or remodelling of the peptidoglycan during the complex life cycle of this sporulating Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium. PBP4a (encoded by the dacC gene) is a low-molecular mass PBP clearly exhibiting in vitro DD-carboxypeptidase activity. We have solved the crystal structure of this protein alone and in complex with a peptide (D-alpha-aminopymelyl-epsilon-D-alanyl-D-alanine) that mimics the C-terminal end of the Bacillus peptidoglycan stem peptide. PBP4a is composed of three domains: the penicillin-binding domain with a fold similar to the class A beta-lactamase structure and two domains inserted between the conserved motifs 1 and 2 characteristic of the penicillin-recognizing enzymes. The soaking of PBP4a in a solution of D-alpha-aminopymelyl-epsilon-D-alanyl-D-alanine resulted in an adduct between PBP4a and a D-alpha-aminopimelyl-epsilon-D-alanine dipeptide and an unbound D-alanine, i.e. the products of acylation of PBP4a by D-alpha-aminopymelyl-epsilon-D-alanyl-D-alanine with the release of a D-alanine. The adduct also reveals a binding pocket specific to the diaminopimelic acid, the third residue of the peptidoglycan stem pentapeptide of B. subtilis. This pocket is specific for this class of PBPs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre d'Ingénierie des Protéines, Université de Liège, Institut de Physique B5 et Institut de Chimie B6a, Sart Tilman, B-4000 Liège, Belgium. Eric.Sauvage@ulg.ac.be