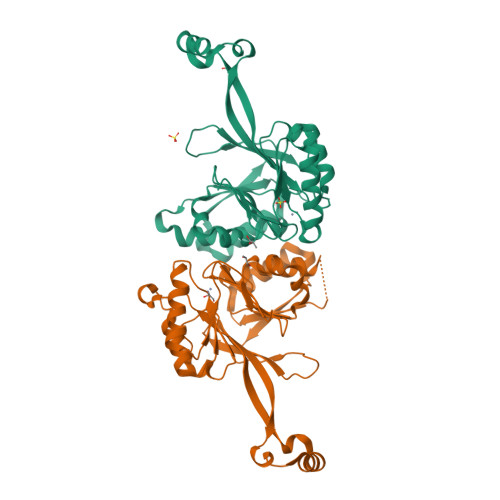
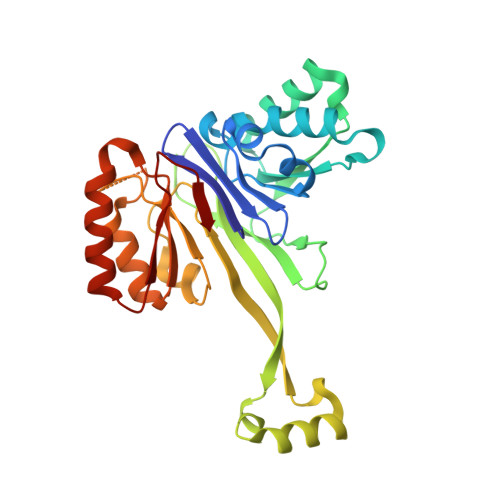
The structure of the flexible arm of Thermotoga maritima tRNase Z differs from those of homologous enzymes
Ishii, R., Minagawa, A., Takaku, H., Takagi, M., Nashimoto, M., Yokoyama, S.(2007) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 63: 637-641
- PubMed: 17671357
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309107033623
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2E7Y - PubMed Abstract:
tRNA 3'-processing endoribonuclease (tRNase Z) is one of the enzymes involved in the 3'-end processing of precursor tRNAs and is a member of the metallo-beta-lactamase superfamily. tRNase Z crystal structures have revealed that the enzyme forms a dimer and has a characteristic domain, named a flexible arm or an exosite, which protrudes from the metallo-beta-lactamase core and is involved in tRNA binding. The refined structure of Thermotoga maritima tRNase Z has been determined at 1.97 A resolution, revealing the structure of the flexible arm and the zinc-bound active site. The structure of the flexible arm of T. maritima tRNase Z is distinct from those of the Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli tRNase Zs. A comparison of the three tRNase Z structures revealed differences in the dimer orientation, which may be related to the unique cleavage-site specificity of T. maritima tRNase Z.
Organizational Affiliation:
RIKEN Genomic Sciences Center, Tsurumi, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.