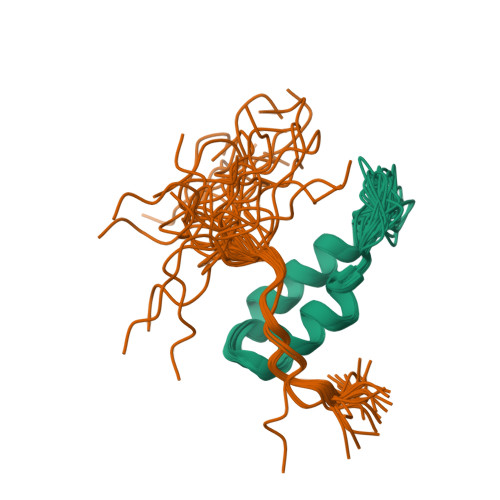
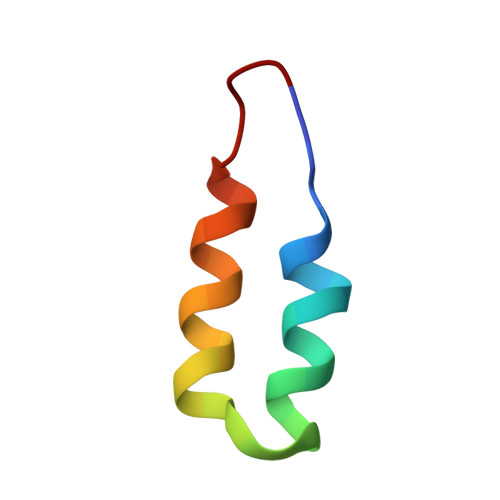
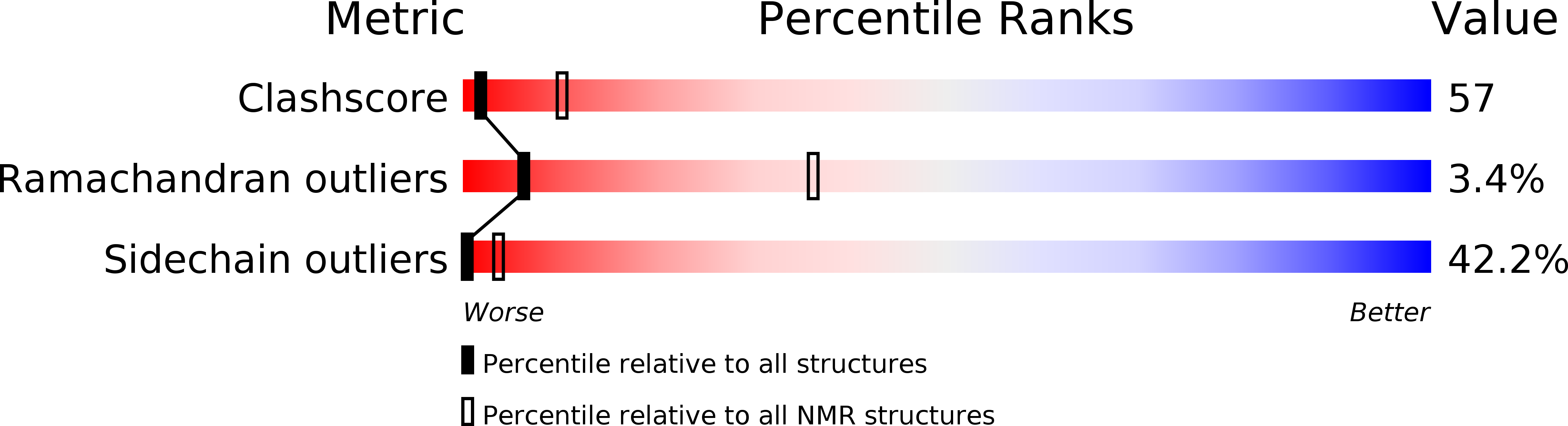Structural Basis of the Interaction between P-Element Somatic Inhibitor and U1-70K Essential for the Alternative Splicing of P-Element Transposase.
Ignjatovic, T., Yang, J.-C., Butler, J., Neuhaus, D., Nagai, K.(2005) J Mol Biology 351: 52
- PubMed: 15990112
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.04.077
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BN5, 2BN6 - PubMed Abstract:
P-element transposition in Drosophila is regulated by tissue-specific alternative splicing of the P-element transposase pre-mRNA. In somatic cells, the P-element somatic inhibitor (PSI) protein binds to exon 3 of the pre-mRNA and recruits U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) to the F1 pseudo-splice site. This abrogates binding of U1 snRNP to the genuine 5' splice site, thereby preventing excision of the third intron. Two homologous short sequences, referred to as the A and B boxes, near the C terminus of PSI bind to U1-70k protein within U1 snRNP. We have now mapped the AB box-binding site of U1-70k to a short proline-rich sequence at the C terminus. Our NMR study shows that the B box forms an anti-parallel helical hairpin in which four highly conserved aromatic residues form a cluster on one face of the first helix. This hydrophobic cluster interacts extensively with the proline-rich region of the U1-70k protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, UK.