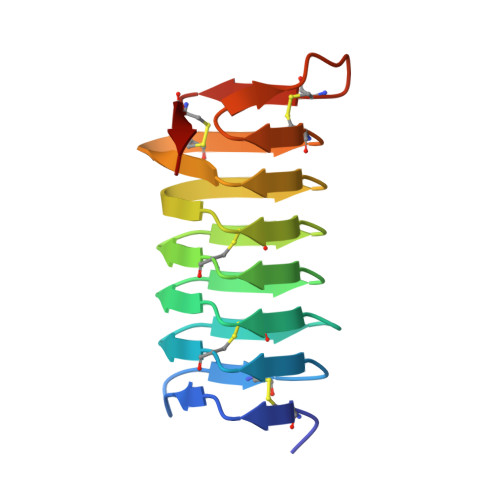
A beta-helical antifreeze protein isoform with increased activity: structural and functional insights
Leinala, E.K., Davies, P.L., Doucet, D., Tyshenko, M.G., Walker, V.K., Jia, Z.(2002) J Biological Chem 277: 33349-33352
- PubMed: 12105229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205575200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M8N - PubMed Abstract:
The insect spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana)(Cf) produces a number of isoforms of its highly active antifreeze protein (CfAFP). Although most of the CfAFP isoforms are in the 9-kDa range, isoforms containing a 30- or 31-amino acid insertion have also been identified. Here we describe the functional and structural analysis of a selected long isoform, CfAFP-501. X-ray crystal structure determination reveals that the 31-amino acid insertion found in CfAFP-501 forms two additional loops within its highly regular beta-helical structure. This effectively extends the area of the two-dimensional Thr array and ice-binding surface of the protein. The larger isoform has 3 times the thermal hysteresis activity of the 9-kDa CfAFP-337. As well, a deletion of the 31-amino acid insertion within CfAFP-501 to form CfAFP-501-Delta-2-loop, results in a protein with reduced activity similar to the shorter CfAFP isoforms. Thus, the enhanced antifreeze activity of CfAFP-501 is directly correlated to the length of its beta-helical structure and hence the size of its ice-binding face.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departments of Biochemistry and Biology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, K7L 3N6 Canada.