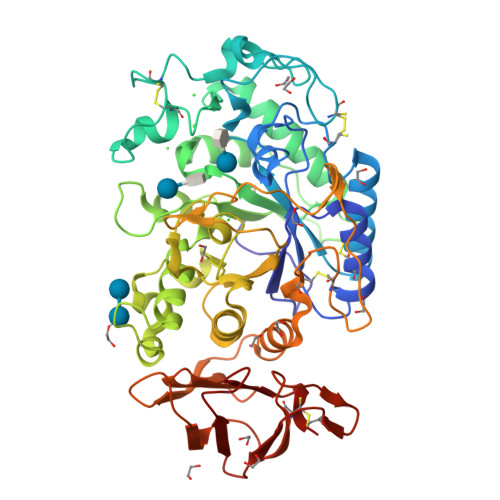
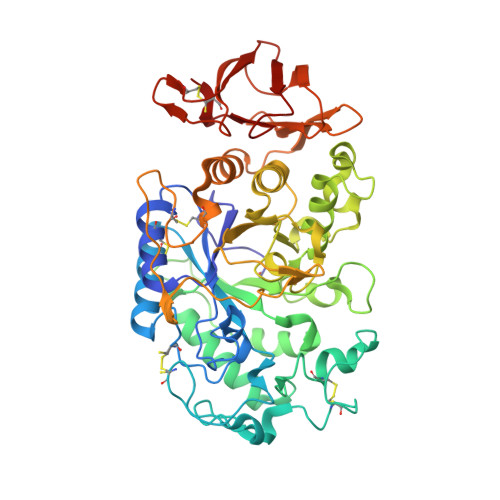
Enzyme-catalyzed condensation reaction in a mammalian alpha-amylase. High-resolution structural analysis of an enzyme-inhibitor complex
Qian, M., Nahoum, V., Bonicel, J., Bischoff, H., Henrissat, B., Payan, F.(2001) Biochemistry 40: 7700-7709
- PubMed: 11412124
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0102050
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HX0 - PubMed Abstract:
Mammalian alpha-amylases catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-linked glucose polymers according to a complex processive mechanism. We have determined the X-ray structures of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase complexes with the smallest molecule of the trestatin family (acarviosine-glucose) which inhibits porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase and yet is not hydrolyzed by the enzyme. A structure analysis at 1.38 A resolution of this complex allowed for a clear identification of a genuine single hexasaccharide species composed of two alpha-1,4-linked original molecules bound to the active site of the enzyme. The structural results supported by mass spectrometry experiments provide evidence for an enzymatically catalyzed condensation reaction in the crystal.
Organizational Affiliation:
Architecture et Fonction des Macromolécules Biologiques, UMR 6098, CNRS and Universities Aix-Marseille I and II, 31 Chemin Joseph Aiguier, 13402 Marseille, France.