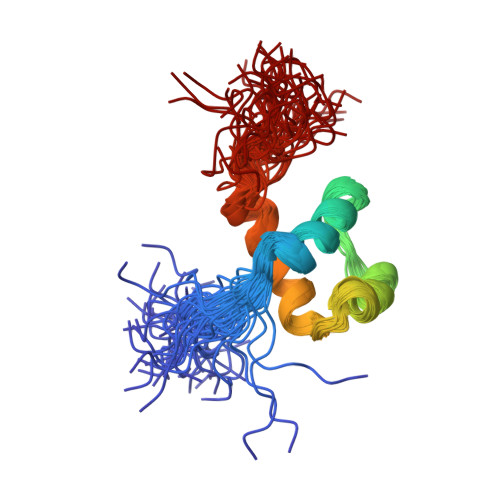
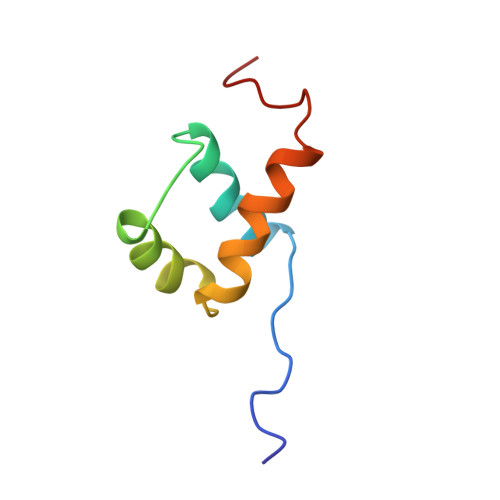
The solution structure of the homeodomain of the rat insulin-gene enhancer protein isl-1. Comparison with other homeodomains.
Ippel, H., Larsson, G., Behravan, G., Zdunek, J., Lundqvist, M., Schleucher, J., Lycksell, P.O., Wijmenga, S.(1999) J Mol Biology 288: 689-703
- PubMed: 10329173
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.2718
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BW5 - PubMed Abstract:
Homeodomains are one of the key families of eukaryotic DNA-binding motifs and provide an important model system for DNA recognition. We have determined a high-quality nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structure of the DNA-binding homeodomain of the insulin gene enhancer protein Isl-1 (Isl-1-HD). It forms the first solution structure of a homeodomain from the LIM family. It contains a well-defined inner core (residues 12-55) consisting of the classical three-helix structure observed in other homeodomains. The N terminus is unstructured up to residue 8, while the C terminus gradually becomes unstructured from residue 55 onwards. Some flexibility is evident in the loop parts of the inner core. Isl-1-HD has, despite its low sequence identity (23-34 %), a structure that is strikingly similar to that of the other homeodomains with known three-dimensional structures. Detailed analysis of Isl-1-HD and the other homeodomains rationalizes the differences in their temperature stability and explains the low stability of the Isl-1-HD in the free state (tm 22-30 degrees C). Upon DNA binding, a significant stabilization occurs (tm>55 degrees C). The low stability of Isl-1-HD (and other mammalian homeodomains) suggests that in vivo Isl-1-HD recognizes its cognate DNA from its unfolded state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Umeâ University, Umeâ, S 901 87, Sweden.