❮
Member 1 of 13
❯
Explore in 3D: Sequence Alignments
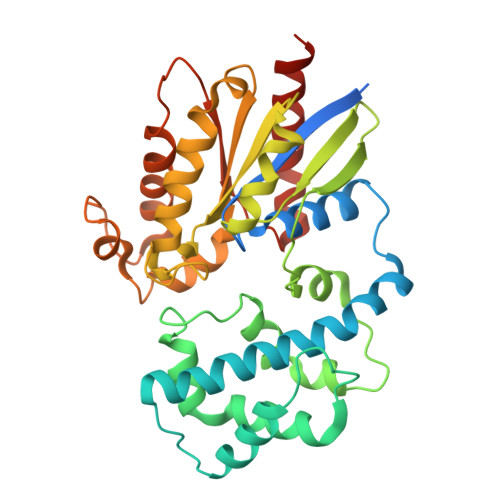
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha
UniProtKB accession: P21279
Grouped By: Matching UniProtKB accession
Group Content:
Polymer Entities matching query 13
Go to UniProtKB: P21279
UniProtKB description: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in numerous signaling cascades (PubMed:20966218, PubMed:9687499). The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state (PubMed:20966218). Signaling by an activated GPCR promotes GDP release and GTP binding (PubMed:20966218). The alpha subunit has a low GTPase activity that converts bound GTP to GDP, thereby terminating the signal (PubMed:20966218). Both GDP release and GTP hydrolysis are modulated by numerous regulatory proteins (PubMed:20966218). Signaling is mediated via phospholipase C-beta-dependent inositol lipid hydrolysis for signal propagation: activates phospholipase C-beta: following GPCR activation, GNAQ activates PLC-beta (PLCB1, PLCB2, PLCB3 or PLCB4), leading to production of diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) (PubMed:20966218). Required for platelet activation (PubMed:9296496). Regulates B-cell selection and survival and is required to prevent B-cell-dependent autoimmunity (PubMed:20624888). Regulates chemotaxis of BM-derived neutrophils and dendritic cells (in vitro) (PubMed:17938235). Transduces FFAR4 signaling in response to long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) (By similarity). Together with GNA11, required for heart development (PubMed:9687499).
Group Members:
Query History
❮
1 / 1
❯
Release Date:
Structure Features
Determination Methodology
Sequence Features
Number of Source Taxonomies
Experimental Features
Experimental Method
Resolution
Organisms
Organism
Taxonomy
Protein Domains
SCOP/SCOPe Domain
CATH Domain
ECOD Domain
PFAM Domain
InterPro Domain
Function
Enzyme Classification
GO Molecular Function
[ 4+ ]
GO Biological Process
[ 24+ ]
GO Cellular Component
[ 7+ ]














