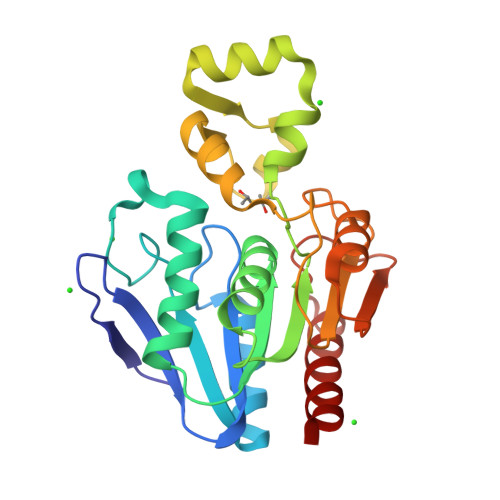
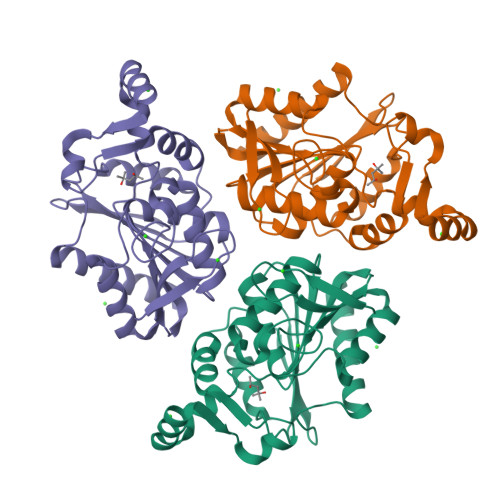
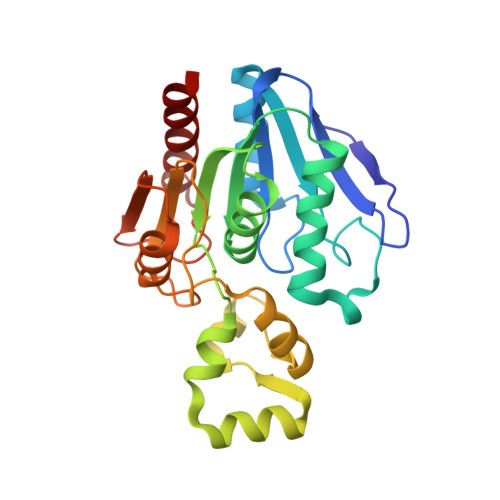
ABHD10 is an S-depalmitoylase affecting redox homeostasis through peroxiredoxin-5.
Cao, Y., Qiu, T., Kathayat, R.S., Azizi, S.A., Thorne, A.K., Ahn, D., Fukata, Y., Fukata, M., Rice, P.A., Dickinson, B.C.(2019) Nat Chem Biol 15: 1232-1240
- PubMed: 31740833
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0399-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NY9 - PubMed Abstract:
S-Palmitoylation is a reversible lipid post-translational modification that has been observed on mitochondrial proteins, but both the regulation and functional consequences of mitochondrial S-palmitoylation are poorly understood. Here, we show that perturbing the 'erasers' of S-palmitoylation, acyl protein thioesterases (APTs), with either pan-active inhibitors or a mitochondrial-targeted APT inhibitor, diminishes the antioxidant buffering capacity of mitochondria. Surprisingly, this effect was not mediated by the only known mitochondrial APT, but rather by a resident mitochondrial protein with no known endogenous function, ABHD10. We show that ABHD10 is a member of the APT family of regulatory proteins and identify peroxiredoxin-5 (PRDX5), a key antioxidant protein, as a target of ABHD10 S-depalmitoylase activity. We then find that ABHD10 regulates the S-palmitoylation status of the nucleophilic active site residue of PRDX5, providing a direct mechanistic connection between ABHD10-mediated S-depalmitoylation of PRDX5 and its antioxidant capacity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA.