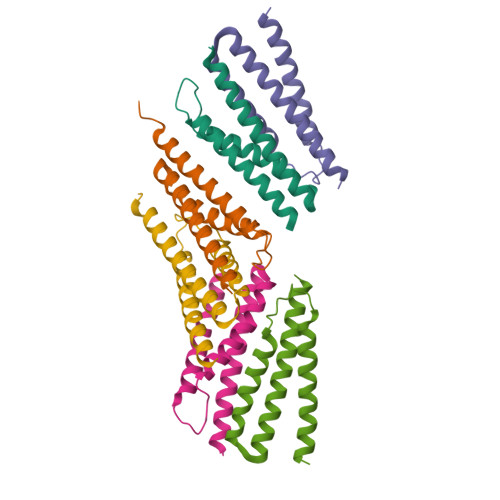
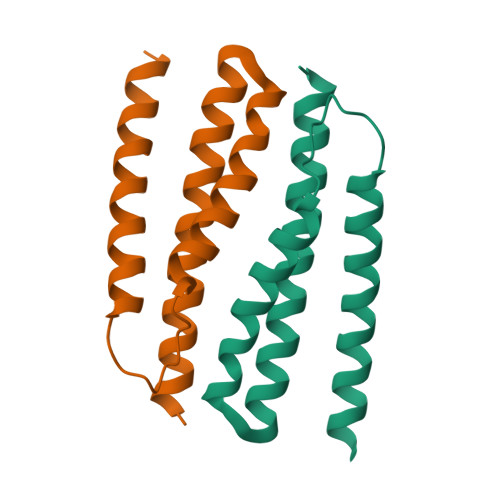
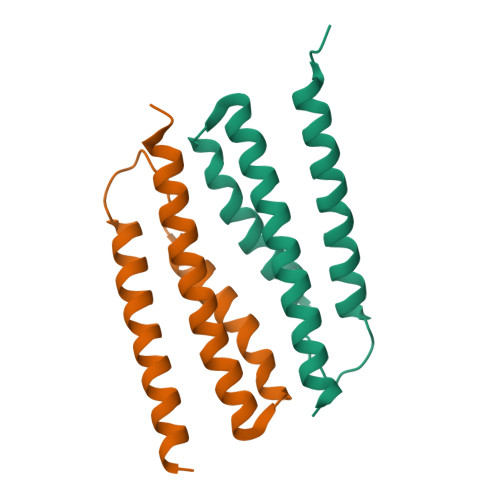
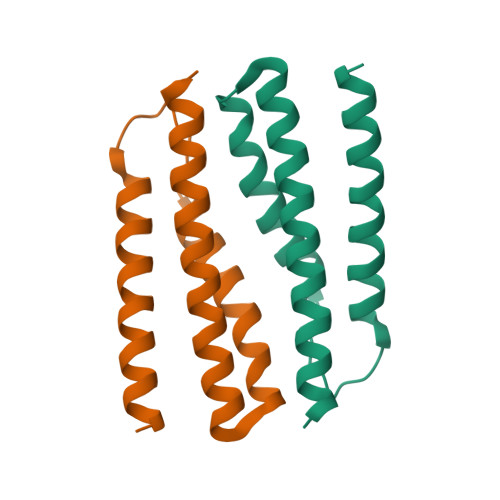
Structural basis for recognition of the type VI spike protein VgrG3 by a cognate immunity protein.
Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Gao, Z., Hu, H., Dong, C., Dong, Y.H.(2014) FEBS Lett 588: 1891-1898
- PubMed: 24751834
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4NSO, 4NSR - PubMed Abstract:
The bacterial type VI secretion system (T6SS) is used by donor cells to inject toxic effectors into receptor cells. The donor cells produce the corresponding immunity proteins to protect themselves against the effector proteins, thereby preventing their self-intoxication. Recently, the C-terminal domain of VgrG3 was identified as a T6SS effector. Information on the molecular mechanism of VgrG3 and its immunity protein TsaB has been lacking. Here, we determined the crystal structures of native TsaB and the VgrG3C-TsaB complex. VgrG3C adopts a canonical phage-T4-lysozyme-like fold. TsaB interacts with VgrG3C through molecular mimicry, and inserts into the VgrG3C pocket.
Organizational Affiliation:
Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, People's Republic of China; School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, 96 Jinzhai Road, Hefei, Anhui 230027, People's Republic of China.