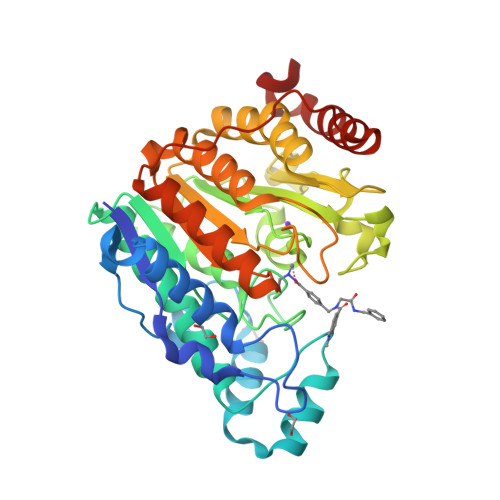
Exploring Alternative Zinc-Binding Groups in Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors Uncovers DS-103 as a Potent Ethylhydrazide-Based HDAC Inhibitor with Chemosensitizing Properties.
Stopper, D., Biermann, L., Watson, P.R., Li, J., Konig, B., Gaynes, M.N., Pessanha de Carvalho, L., Klose, J., Hanl, M., Hamacher, A., Schaker-Hubner, L., Ramsbeck, D., Held, J., Christianson, D.W., Kassack, M.U., Hansen, F.K.(2025) J Med Chem 68: 4426-4452
- PubMed: 39946728
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02373
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9DM6 - PubMed Abstract:
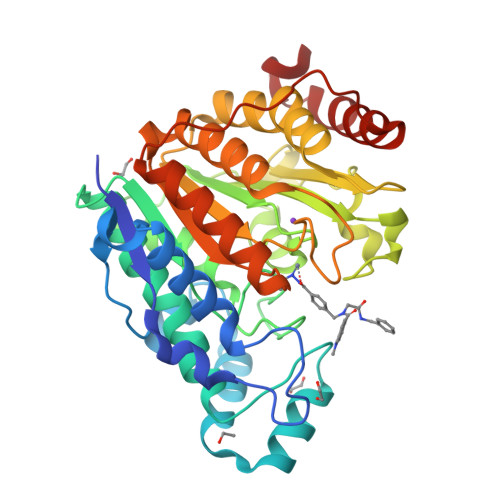
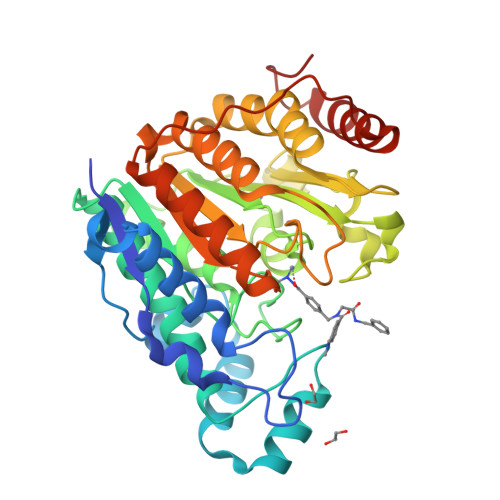
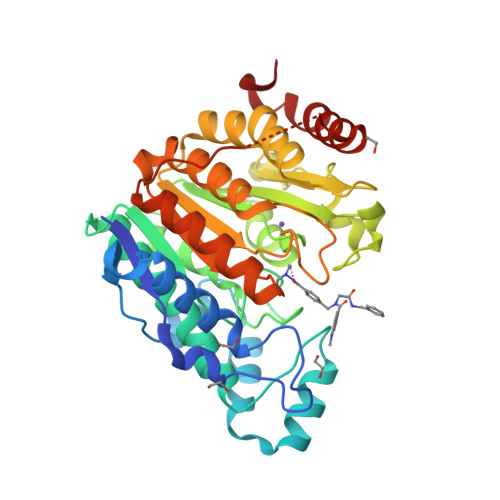
In this work, we synthesized a series of peptoid-based histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with variations in the linker region and zinc-binding groups. All compounds were investigated for their HDAC inhibition, antiplasmodial activity, and cytotoxicity against native and cisplatin-resistant carcinoma cell lines. The ethylhydrazide 20 ( DS-103 ) proved to be the most effective compound in these primary screenings. DS-103 showed nanomolar inhibition of class I HDACs and of HDAC6 (class IIb). To further investigate the binding mode of DS-103 , a crystal structure of DS-103 in complex with HDAC6 was obtained, which represents the first reported crystal structure of an alkylhydrazide in complex with an HDAC enzyme. Importantly, DS-103 completely reversed cisplatin resistance in two different platinum-resistant solid cancer cell lines and demonstrated strong synergism with cisplatin. The synergistic anticancer effects are mediated by increased DNA damage and p21 expression, resulting in caspase-mediated apoptosis and cell death.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical and Cell Biological Chemistry, Pharmaceutical Institute, University of Bonn, 53121 Bonn, Germany.