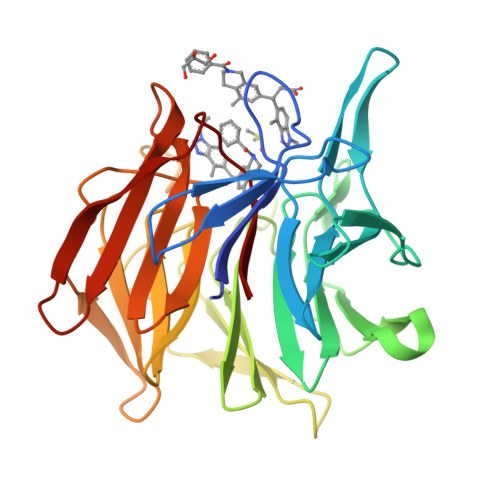
Design, synthesis and identification of novel, orally bioavailable non-covalent Nrf2 activators.
Ma, B., Lucas, B., Capacci, A., Lin, E.Y., Jones, J.H., Dechantsreiter, M., Enyedy, I., Marcotte, D., Xiao, G., Li, B., Richter, K.(2020) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30: 126852-126852
- PubMed: 31898999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.126852
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TYM, 6TYP - PubMed Abstract:
Nrf2 is a transcription factor regulating expression of the Phase II Antioxidant Response and plays an important role in neuroprotection and detoxification. Nrf2 activation is inhibited by interaction with Keap1. Covalent Keap1 inhibitors such as dimethyl fumarate (DMF) and RTA-408 are either on the market or in late stage clinical trials which implies potential benefit of Nrf2 activation. Activation of Nrf2 by disrupting Nrf2-Keap1 interaction through a non-covalent small molecule is an attractive approach with the promise of greater selectivity. However, there are no known non-covalent Nrf2 activators with acceptable pharmacokinetic properties to test the hypothesis in vivo. Based on our early reported work, using structural-based design, followed by extensive SAR exploration, we have identified a novel series of non-covalent Nrf2 activators, with sub-nanomolar binding affinity on Keap1 and single digit nanomolar activity in an astrocyte assay. A representative analog shows excellent oral PK and good Nrf2-dependent gene inductions in kidney. These results provide a peripheral in vivo tool compound to validate the biology of non-covalent activation of Nrf2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Medicinal Chemistry, Biogen, 225 Binney Street, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA. Electronic address: bin.ma@biogen.com.