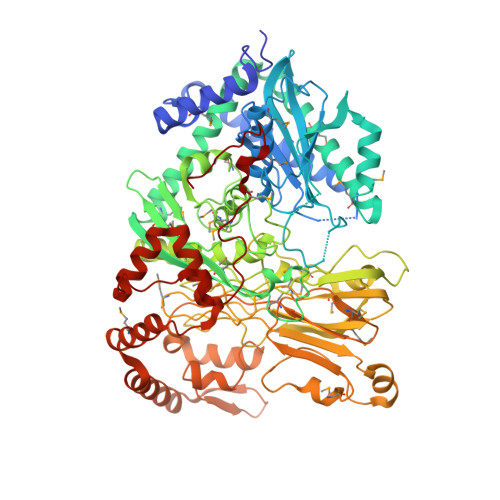
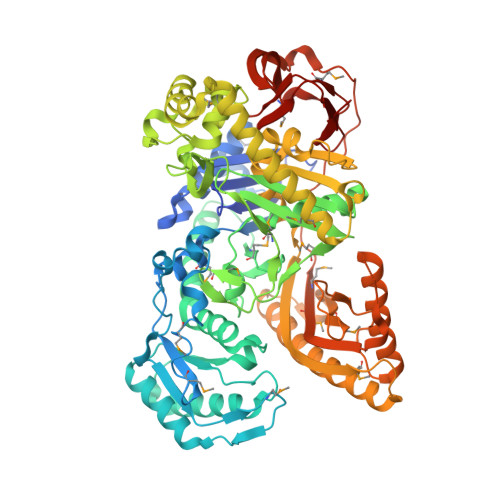
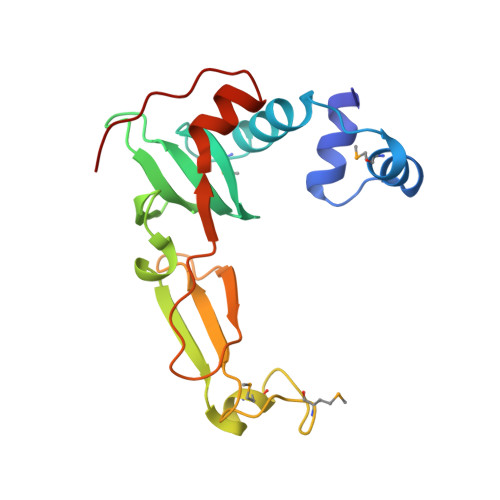
Structural Basis for the Mechanism of ATP-Dependent Acetone Carboxylation.
Mus, F., Eilers, B.J., Alleman, A.B., Kabasakal, B.V., Wells, J.N., Murray, J.W., Nocek, B.P., DuBois, J.L., Peters, J.W.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 7234-7234
- PubMed: 28775283
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06973-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5M45, 5SVB, 5SVC - PubMed Abstract:
Microorganisms use carboxylase enzymes to form new carbon-carbon bonds by introducing carbon dioxide gas (CO 2 ) or its hydrated form, bicarbonate (HCO 3 - ), into target molecules. Acetone carboxylases (ACs) catalyze the conversion of substrates acetone and HCO 3 - to form the product acetoacetate. Many bicarbonate-incorporating carboxylases rely on the organic cofactor biotin for the activation of bicarbonate. ACs contain metal ions but not organic cofactors, and use ATP to activate substrates through phosphorylation. How the enzyme coordinates these phosphorylation events and new C-C bond formation in the absence of biotin has remained a mystery since these enzymes were discovered. The first structural rationale for acetone carboxylation is presented here, focusing on the 360 kDa (αβγ) 2 heterohexameric AC from Xanthobacter autotrophicus in the ligand-free, AMP-bound, and acetate coordinated states. These structures suggest successive steps in a catalytic cycle revealing that AC undergoes large conformational changes coupled to substrate activation by ATP to perform C-C bond ligation at a distant Mn center. These results illustrate a new chemical strategy for the conversion of CO 2 into biomass, a process of great significance to the global carbon cycle.
Organizational Affiliation:
Insitutite of Biological Chemistry, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, 99164, USA.