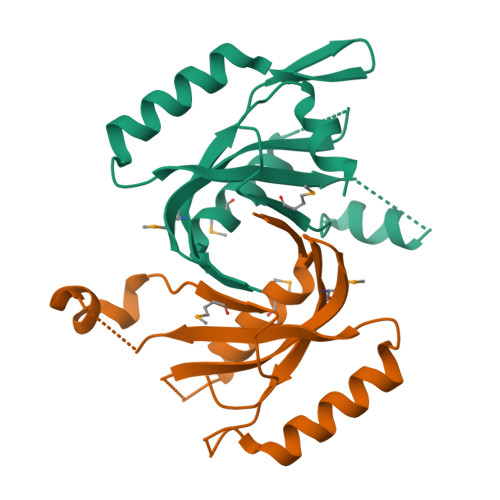
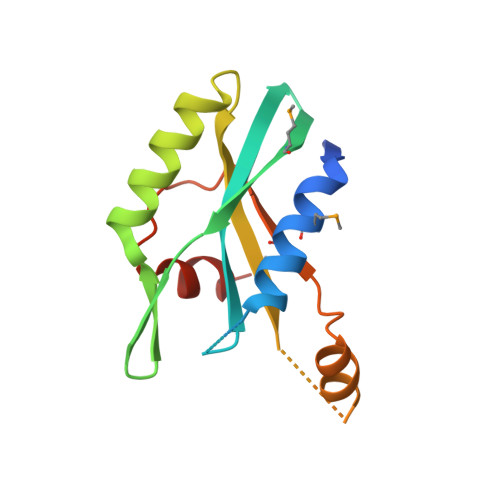
The crystal structure of the MPN domain from the COP9 signalosome subunit CSN6
Zhang, H., Gao, Z.Q., Wang, W.J., Liu, G.F., Shtykova, E.V., Xu, J.H., Li, L.F., Su, X.D., Dong, Y.H.(2012) FEBS Lett 586: 1147-1153
- PubMed: 22575649
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.03.029
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4E0Q - PubMed Abstract:
The COP9 signalosome (CSN) is a multiprotein complex containing eight subunits and is highly conserved from fungi to human. CSN is proposed to widely participate in many physiological processes, including protein degradation, DNA damage response and signal transduction. Among those subunits, only CSN5 and CSN6 belong to JAMM family. CSN5 possesses isopeptidase activity, but CSN6 lacks this ability. Here we report the 2.5Å crystal structure of MPN domain from Drosophila melanogaster CSN6. Structural comparison with other MPN domains, along with bioinformation analysis, suggests that MPN domain from CSN6 may serve as a scaffold instead of a metalloprotease.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, and Biodynamic Optical Imaging Center (BIOPIC), School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China.